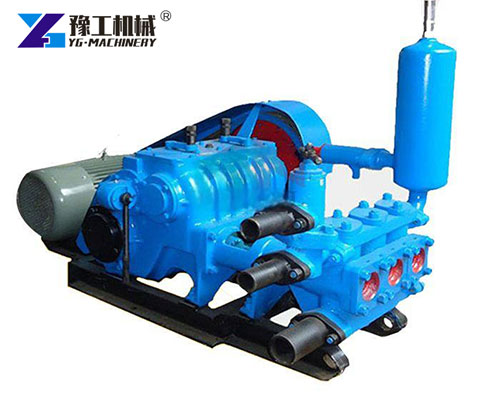
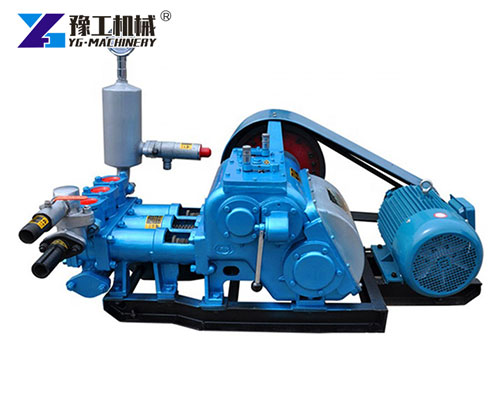


What Is a Mud Pump?
A mud pump for sale is a critical piece of equipment in drilling systems. It is used to circulate drilling fluid, also known as drilling mud, down the drill string and back up the annulus. This circulation system serves multiple functions, including cooling the bit, carrying cuttings to the surface, and stabilizing the wellbore.
Drilling operations—whether for oil, gas, or water—require a dependable mud pump to maintain proper hydraulic balance, bit cleaning, and formation control throughout the project.
WhatsApp/WeChat/Phone: 86 138 3715 9132
Key Technical Parameters of a Mud Pump for Sale
| Model | BW150 | BW160 | BW250 | BW320 |
| Max. Flow(L/min) | 150 | 160 | 250 | 320 |
| Max. Pressure(Mpa) | 7 | 10 | 6 | 8 |
| Power(KW) | 7.5 | 11 | 15 | 30 |
| Suction Pipe Diameter | φ51 | φ51 | φ76 | φ76 |
| Drain Pipe Diameter | φ32 | φ32 | φ32 | φ32 |
| Weight(Kg) | 560 | 480 | 760 | 1000 |
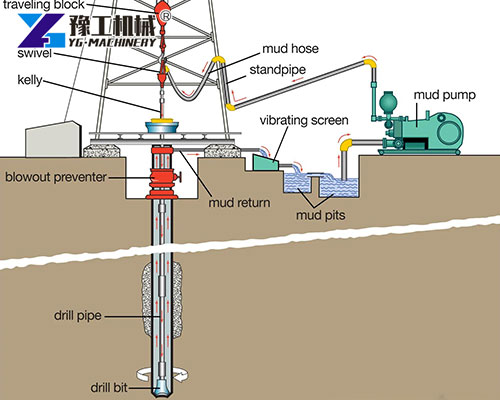
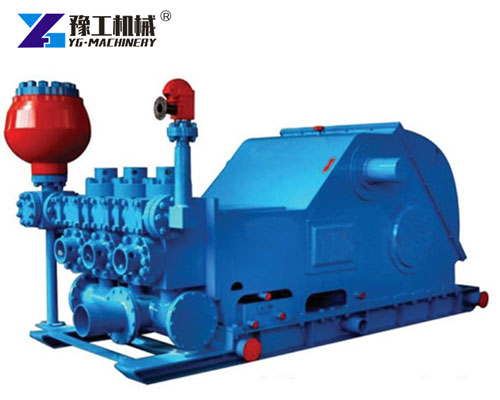
Structural Components of a Mud Pump
A standard Mud Pump for Sale is composed of multiple robust sections designed for continuous operation:
- Power End: Converts mechanical energy from the engine into linear piston motion.
- Fluid End: Handles the pumping and pressurizing of mud via pistons or plungers.
- Crankshaft & Connecting Rods: Transmit energy from the motor to the pistons.
- Valves & Liners: Direct fluid flow and withstand abrasive wear.
- Suction & Discharge Manifolds: Ensure proper intake and expulsion of mud during circulation.
- Spray System & Cooling Mechanism: Reduce temperature and wear in high-speed operations.
Each part must be maintained properly to ensure consistent performance and reduce unplanned downtime.


Working Principle of a Drilling Mud Pump
A drilling mud pump works using a reciprocating piston or plunger to draw drilling fluid from a reservoir and push it down the drill pipe. The operating cycle involves:
- Suction Stroke: The piston moves backward, creating negative pressure and drawing in mud.
- Discharge Stroke: The piston pushes forward, forcing the mud through the discharge line into the well.
- Valve Control: Inlet and outlet valves open and close in rhythm with the piston to ensure one-way flow.
This process allows for continuous fluid circulation even in deep and high-pressure environments.
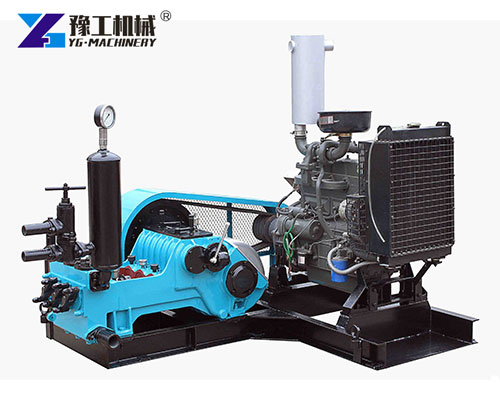
Types of Mud Pumps for Sale by Structure and Drive
Different types of Mud Pumps for Sale suit various drilling conditions. Classification typically includes:
By Structure
- Triplex Mud Pumps: Three pistons, widely used due to high efficiency and low vibration.
- Duplex Mud Pumps: Two pistons, simpler design, suitable for low-to-medium pressure drilling.
- Quintuplex Pumps: Five pistons, ideal for extremely high-pressure applications and longer service life.
By Drive Type
- Diesel Engine Driven: Preferred in remote locations with limited electric supply.
- Electric Motor Driven: Offers cleaner operation and higher energy efficiency.
- Hydraulic Driven: Used for compact or mobile rigs needing precise control.
Special Types
- Shear-Resistant Mud Pumps: Designed to preserve the integrity of polymer-based muds.
- Corrosion-Resistant Models: Built with stainless or coated parts for acidic environments.
- High-Temperature Models: Equipped with seals and cooling systems for geothermal drilling.
How to Select the Right Mud Pump for Your Project
Choosing the ideal Mud Pump for Sale involves considering multiple operational factors:
- Drilling Depth: Deeper wells require pumps with higher flow and pressure ratings.
- Mud Viscosity: Thicker muds need more powerful pumps to maintain flow rate.
- Pump Type Compatibility: Match piston size and stroke speed to the rig’s hydraulic setup.
- Formation Characteristics: Hard or unstable formations may require more robust flow to remove cuttings.
- Power Source Availability: Choose between diesel, electric, or hybrid models based on site conditions.
- Cost and Maintenance: Balance initial investment with spare parts availability and service life.
Making a data-driven decision will ensure smoother drilling operations and reduced maintenance risk.
Mud Pump and Drilling Equipment Matching Guide
| Drilling Equipment Type | Recommended Mud Pump Type | Flow Rate (L/min) | Pressure (MPa) | Drive Mode | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shallow Water Well Drill Rig | Duplex Mud Pump (BW160/BW250) | 160–250 | 1.5–2.5 | Electric/Diesel | Compact and energy-efficient; suitable for low-depth wells. |
| Deep Borehole Drill Rig (>300m) | Triplex Mud Pump (BW850/1300) | 850–1300 | 3.0–5.0 | Diesel | High-pressure required for deeper formations. |
| Oil & Gas Drilling Rig | Triplex or Quintuplex Pump | 1600–2200+ | 10.0–35.0 | Diesel/Electric | Heavy-duty pumps with advanced cooling and wear-resistant features. |
| Geothermal Drilling Rig | Corrosion-Resistant Mud Pump | 850–1500 | 5.0–10.0 | Diesel/Electric | Must handle hot and mineral-rich fluids. |
| Horizontal Directional Drilling | Triplex Compact Mud Pump | 400–1000 | 4.0–6.0 | Hydraulic/Electric | Stable flow needed for trenchless borehole support. |
| Mining Exploration Drilling Rig | Medium Triplex Pump (BW450–850) | 450–850 | 3.5–6.0 | Diesel/Electric | Must cope with rock dust and abrasive cuttings. |
| Truck-Mounted Drill Rig | Lightweight Electric Mud Pump | 160–600 | 2.0–3.5 | Electric | Focus on mobility and easy maintenance. |
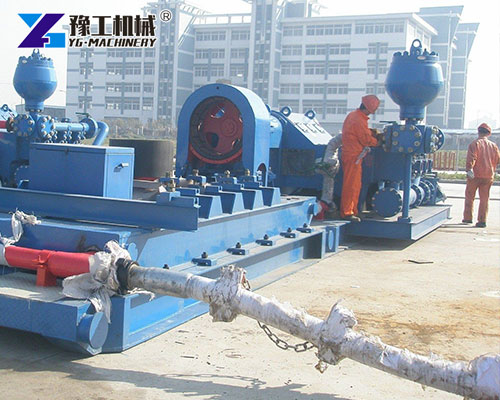
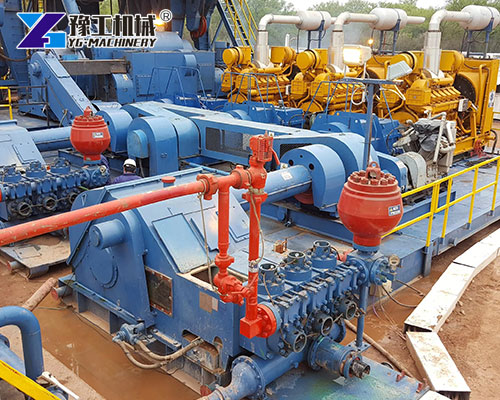


Applications of Mud Pumps for Drilling Rigs
Mud Pumps for Drilling Rigs are used across various drilling projects including:
- Oil and Gas Exploration: Essential for maintaining pressure balance and bit cooling.
- Water Well Drilling: Ensures borehole stability and sediment removal.
- Geothermal Drilling: Handles high-temperature and mineral-rich fluids.
- Horizontal Directional Drilling (HDD): Maintains borehole shape during trenchless operations.
- Mining and Exploration: Circulates drilling fluid through tough rock strata.
A reliable mud pump enhances the overall success rate and efficiency of any drilling process.
Frequently Asked Questions About Mud Pumps
- Q1: What is the typical lifespan of a mud pump?
A: With regular maintenance, liners and pistons last hundreds of hours, while the pump body can function for several years. - Q2: How often should the fluid end be serviced?
A: It depends on usage. For most operations, inspecting seals, valves, and liners every 150–250 hours is recommended. - Q3: Can I switch between diesel and electric drives?
A: Some models allow interchangeable drive systems, but compatibility must be verified with the manufacturer. - Q4: Do mud pumps work with all types of drilling fluids?
A: Most pumps are compatible with water-based and oil-based muds; specialized designs are available for high-viscosity or abrasive fluids. - Q5: How do I avoid pump cavitation?
A: Ensure adequate mud supply and correct suction pipe diameter to maintain stable intake pressure.
WhatsApp/WeChat/Phone: 86 138 3715 9132










